The Comprehensive Guide to Pancreatitis: Understanding Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis
- The Comprehensive Guide to Pancreatitis: Understanding Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis
- Introduction
- Getting to Know the Pancreas
- Acute Pancreatitis: The Sudden Onset
- Chronic Pancreatitis: The Persistent Challenge
- Differentiating Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis
- Conventional Treatment and Prevention
- Prevention Strategies
- Herbal Medicines for Acute & Chronic Pancreatitis
- Lifestyle Modification
- Conclusion
Introduction
Acute & Chronic Pancreatitis is a complex and potentially severe condition that affects the pancreas, an organ crucial for digestion and blood sugar regulation. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore both acute and chronic pancreatitis, highlighting the key differences between these two conditions. We’ll cover practice essentials, clinical presentation, workup, complications, conventional treatments, prevention strategies, herbal remedies for treatment, lifestyle modifications, and conclude with valuable insights for those dealing with pancreatitis.
Getting to Know the Pancreas
Before diving into the specifics of acute and chronic pancreatitis, let’s establish a foundational understanding of the pancreas and its critical role in our bodies.
- The Pancreas Unveiled
The pancreas, a vital organ situated behind the stomach, has a dual role in the human body. It not only produces digestive enzymes that facilitate the breakdown of food but also secretes essential hormones, including insulin, to regulate blood sugar levels.
- The Power of Digestive Enzymes
The pancreas manufactures a variety of enzymes, such as amylase, lipase, and protease, which are released into the small intestine to aid in the digestion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins found in the food we consume.
- Blood Sugar Regulation
Within the pancreas, clusters of cells known as the islets of Langerhans produce hormones like insulin and glucagon. These hormones play a pivotal role in regulating blood sugar levels, ensuring they remain within a healthy range.
Now that we’ve established the pancreas’s essential functions, let’s delve into the specifics of acute and chronic pancreatitis.
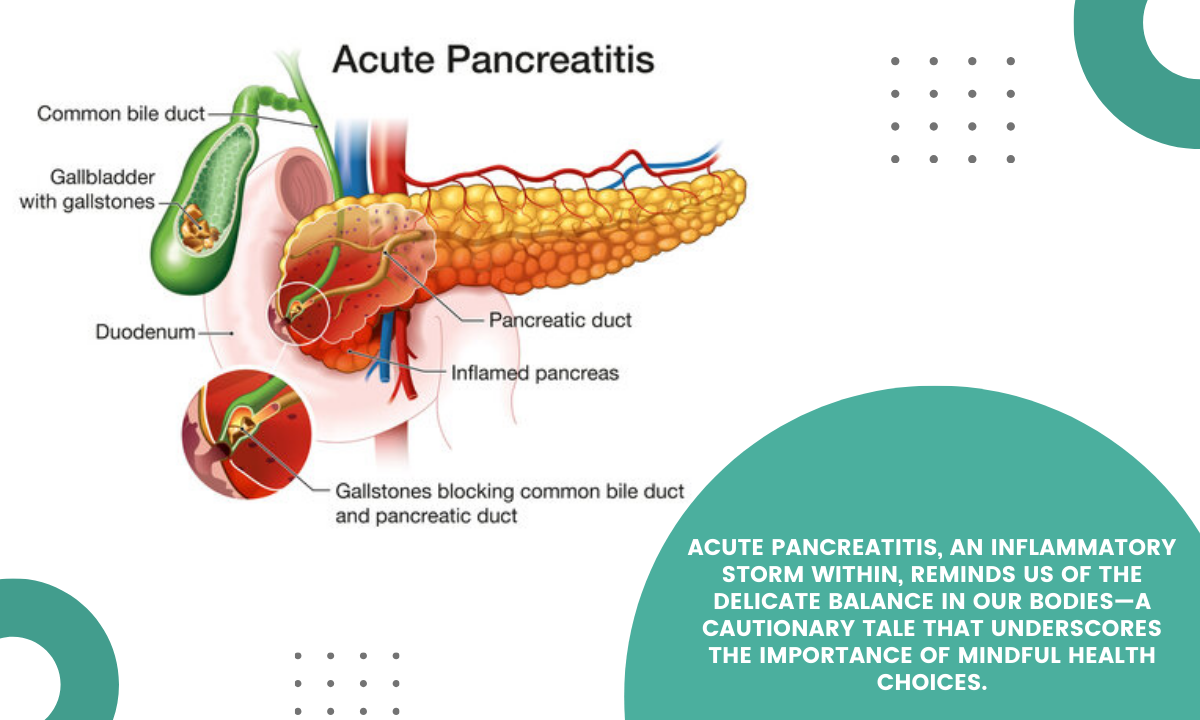
Acute Pancreatitis: The Sudden Onset
Acute pancreatitis is a condition characterized by the abrupt inflammation of the pancreas. It can manifest as mild discomfort or evolve into a severe illness, potentially leading to complications if left untreated.
Clinical Presentation of Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis typically presents with the following symptoms:
- Severe Abdominal Pain: The hallmark symptom of acute pancreatitis, often described as a constant, dull pain in the upper abdomen that may radiate to the back.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms, often accompanied by a loss of appetite.
- Fever: Some individuals may develop a fever in response to the inflammation.
- Abdominal Tenderness: The abdomen may become tender to the touch, and healthcare providers may notice swelling or bruising around the affected area.
Workup for Acute Pancreatitis
Diagnostic tests used in the workup of acute pancreatitis include:
- Blood Tests: Elevated levels of pancreatic enzymes, such as amylase and lipase, serve as indicators of pancreatitis.
- Imaging Studies: Computed tomography (CT) scans and abdominal ultrasounds help visualize the pancreas and assess the extent of inflammation.
- Endoscopic Tests: In some cases, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) may be necessary to evaluate the pancreatic and bile ducts.
Chronic Pancreatitis: The Persistent Challenge
Chronic pancreatitis is a prolonged inflammatory condition of the pancreas that often results from repeated acute pancreatitis episodes or sustained alcohol abuse. The persistent inflammation and scarring can lead to irreversible damage.
Clinical Presentation of Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by:
- Persistent Abdominal Pain: Individuals with chronic pancreatitis experience recurring or constant abdominal pain.
- Steatorrhea: The pancreas fails to produce enough digestive enzymes, leading to fat malabsorption, which results in pale, foul-smelling stools.
- Weight Loss: Digestive issues can lead to malnutrition and unwanted weight loss.
- Diabetes: Over time, chronic pancreatitis may impair the pancreas’s ability to produce insulin, resulting in diabetes.
Workup for Chronic Pancreatitis
Diagnosing chronic pancreatitis may involve:
- Imaging Studies: Computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and endoscopic ultrasound help evaluate the extent of damage.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests assess pancreatic function and monitor blood sugar levels.
Differentiating Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis
It’s crucial to distinguish between acute and chronic pancreatitis as they have distinct characteristics and necessitate different management strategies.
Acute Pancreatitis:
- Sudden inflammation onset.
- Symptoms may resolve with appropriate treatment.
- Severe or recurring acute pancreatitis may lead to chronic pancreatitis.
Chronic Pancreatitis:
- Prolonged, persistent inflammation.
- Symptoms are often recurrent and may worsen over time.
- Irreversible pancreatic damage can occur.
Conventional Treatment and Prevention
The management of pancreatitis involves:
- Acute Pancreatitis Treatment
- Hospitalization: Severe cases require hospitalization for supportive care and complications management.
- NPO (Nil Per Os): Fasting may be required to allow the pancreas to rest and heal.
- Pain Management: Pain relief is crucial, and medications are prescribed to manage pain.
- Fluid Replacement: Intravenous fluids are administered to maintain hydration.
- Dietary Changes: Once symptoms improve, a gradual transition to a low-fat diet is recommended.
- Addressing Underlying Causes: The underlying cause, such as gallstone removal, should be addressed.
- Chronic Pancreatitis Management
- Pain Management: Medications or interventions are utilized to manage chronic pain.
- Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement: Enzyme supplements are prescribed to aid digestion.
- Nutritional Support: Dietary counseling and nutritional supplements help manage malabsorption.
- Abstinence from Alcohol: For those with alcohol-induced chronic pancreatitis, abstaining from alcohol is crucial.
- Diabetes Management: Blood sugar levels are monitored, and insulin may be used if necessary.
Prevention Strategies
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: If alcohol is a contributing factor, moderation or abstinence is advised.
- Healthy Diet: Adopting a balanced diet low in saturated fats supports pancreatic health.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is essential for pancreatitis prevention.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: Treating underlying conditions such as high triglycerides and gallstones reduces the risk.
Herbal Medicines for Acute & Chronic Pancreatitis
While herbal remedies are generally not the primary treatment for acute & chronic pancreatitis, some may offer supportive benefits:
- Turmeric (Curcumin): Renowned for its anti-inflammatory properties, turmeric may help reduce inflammation.
- Milk Thistle (Silymarin): It may support liver health and potentially benefit those with alcohol-induced pancreatitis.
However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before using herbal remedies, especially if you have an underlying medical condition or are taking other medications.
Lifestyle Modification
Lifestyle modifications can significantly impact pancreatitis management:
- Healthy Diet: Adopting a balanced diet low in saturated fats and processed foods can support overall health.
- Abstinence from Alcohol: For individuals with alcohol-induced pancreatitis, avoiding alcohol is crucial.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can support overall well-being and help maintain a healthy weight.
- Stress Reduction: Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can benefit those with chronic pancreatitis.
Conclusion
Pancreatitis is a complex condition with both acute and chronic forms, each requiring unique approaches to diagnosis and management. Understanding the key differences between these conditions is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals.
Timely and accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and prevention strategies are vital for improving the quality of life for those affected by pancreatitis. While herbal medicines and lifestyle modifications can play supportive roles, they should always be used under the guidance of healthcare providers.
In conclusion, with the right approach, individuals with pancreatitis can effectively manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications, ultimately leading to better overall health and well-being.