An Easy-To-Understand Guide on Alcoholic Hepatitis: Exploring the Role of Herbal Medicine in Treating Alcoholic Hepatitis
- An Easy-To-Understand Guide on Alcoholic Hepatitis: Exploring the Role of Herbal Medicine in Treating Alcoholic Hepatitis
- Introduction
- Practice Essentials of Alcoholic Hepatitis
- Clinical Presentation of Alcoholic Hepatitis
- Differential Diagnosis
- Workup for Alcoholic Hepatitis
- Conventional Treatment for Alcoholic Hepatitis
- Prevention of Alcoholic Hepatitis
- Herbal Medicines for Alcoholic Hepatitis
- Lifestyle Modification for Alcoholic Hepatitis
- Conclusion
Introduction
Alcoholic Hepatitis is a liver condition caused by excessive alcohol consumption. It is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that requires careful management. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of Alcoholic Hepatitis, including practice essentials, clinical presentation, differential diagnosis, workup, conventional treatment, prevention, herbal medicines, lifestyle modifications, and conclude with valuable insights for those dealing with this condition.

Practice Essentials of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Understanding the fundamental aspects of Alcoholic Hepatitis is essential for healthcare professionals and patients alike. Let’s explore the practice essentials of this critical condition.
- Definition and Etiology
Alcoholic Hepatitis is an inflammatory liver condition caused by chronic, heavy alcohol consumption. It is a manifestation of alcoholic liver disease, a spectrum of liver damage ranging from fatty liver to cirrhosis. The condition occurs when the liver becomes inflamed due to alcohol-related injury.
- Prevalence
The prevalence of Alcoholic Hepatitis varies worldwide, but it is a significant public health concern. It is more common in individuals with a history of heavy alcohol use, with varying levels of alcohol intake required to trigger the condition.
- Risk Factors
The primary risk factor for Alcoholic Hepatitis is excessive alcohol consumption. Other risk factors include genetics, gender (men are more commonly affected), and coexisting liver diseases.
Clinical Presentation of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic Hepatitis presents with a range of symptoms and signs that reflect the liver’s inability to function properly. The clinical presentation may include:
- Jaundice
Jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, is a common symptom. It occurs due to the accumulation of bilirubin in the bloodstream.
- Hepatomegaly
An enlarged liver is often observed during physical examination.
- Abdominal Pain
Patients may experience pain in the upper right abdomen, which can be tender to the touch.
- Anorexia and Weight Loss
Loss of appetite and unintentional weight loss are common symptoms.
- Fatigue and Weakness
Patients often report profound fatigue and weakness.
- Ascites and Edema
Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen (ascites) and swelling of the legs (edema) can occur.
- Spider Angiomas
These are small, red spider-like blood vessels that may develop on the skin.
- Palmar Erythema
The palms of the hands may develop a reddish appearance.
It’s important to note that Alcoholic Hepatitis can range from mild to severe, and severe cases can lead to life-threatening complications. Therefore, immediate medical attention is crucial.
Differential Diagnosis
Alcoholic Hepatitis shares some clinical features with other medical conditions, and it’s essential to consider these in the differential diagnosis. Conditions that may mimic Alcoholic Hepatitis include:
- Viral Hepatitis
Acute viral hepatitis can present with jaundice and liver dysfunction, similar to Alcoholic Hepatitis. Distinguishing between the two is crucial for treatment.
- Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Medications or toxins can lead to liver injury and may present with symptoms similar to Alcoholic Hepatitis.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD can cause liver inflammation and may mimic Alcoholic Hepatitis. It often occurs in individuals with obesity and metabolic syndrome.
- Cirrhosis
Advanced liver cirrhosis can lead to symptoms similar to those of Alcoholic Hepatitis.
A comprehensive medical evaluation, including history, clinical examination, and laboratory tests, is essential to distinguish Alcoholic Hepatitis from these conditions.
Workup for Alcoholic Hepatitis
The workup for Alcoholic Hepatitis involves a series of diagnostic tests and procedures to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of liver damage:
- Medical History and Physical Examination
A detailed medical history and thorough physical examination are conducted to identify potential risk factors, symptoms, and signs of Alcoholic Hepatitis.
- Laboratory Tests
- Liver Function Tests: These tests evaluate the liver’s synthetic and detoxifying functions. Elevated levels of liver enzymes (AST and ALT) and bilirubin are common in Alcoholic Hepatitis.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test helps assess anemia and platelet count, which can be affected in Alcoholic Hepatitis.
- Coagulation Profile: Assessment of blood clotting parameters helps evaluate the liver’s ability to produce clotting factors.
- Serology: Blood tests for viral hepatitis markers (e.g., hepatitis B and C) are essential to identify infectious causes.
- Toxicology Screen: Detecting drugs or toxins in the bloodstream is crucial, especially in cases of drug-induced liver injury.
- Imaging Studies
- Ultrasound: Abdominal ultrasound can assess liver size, look for structural abnormalities, and identify ascites.
- CT or MRI: These imaging techniques may be used to evaluate liver and surrounding structures, helping to identify structural abnormalities.
- Liver Biopsy
While less common, a liver biopsy may be necessary to assess the degree of liver damage and confirm the diagnosis.
The results of these diagnostic tests guide healthcare providers in diagnosing Alcoholic Hepatitis and determining the appropriate treatment approach.
Conventional Treatment for Alcoholic Hepatitis
The treatment of Alcoholic Hepatitis is multifaceted and varies depending on the severity of the condition. Common interventions include:
- Abstinence from Alcohol
The most critical aspect of treatment is complete abstinence from alcohol. This is essential to prevent further liver damage and promote recovery.
- Supportive Care
- Nutritional Support: Malnutrition is common in Alcoholic Hepatitis, and patients may require intravenous (IV) nutrition to address deficiencies.
- Management of Complications: Ascites, encephalopathy, and other complications are treated as they arise.
- Medications
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroid medications, such as prednisone, may be prescribed for severe cases of Alcoholic Hepatitis to reduce inflammation and improve liver function.
- Pentoxifylline: This medication may be used as an alternative to corticosteroids in certain cases.
- Liver Transplantation
In severe cases of Alcoholic Hepatitis, where liver function is severely compromised and other treatments have failed, liver transplantation may be considered.
- Monitoring and Surveillance
Regular monitoring of liver function and clinical status is essential to assess the patient’s response to treatment and make timely decisions regarding transplantation.
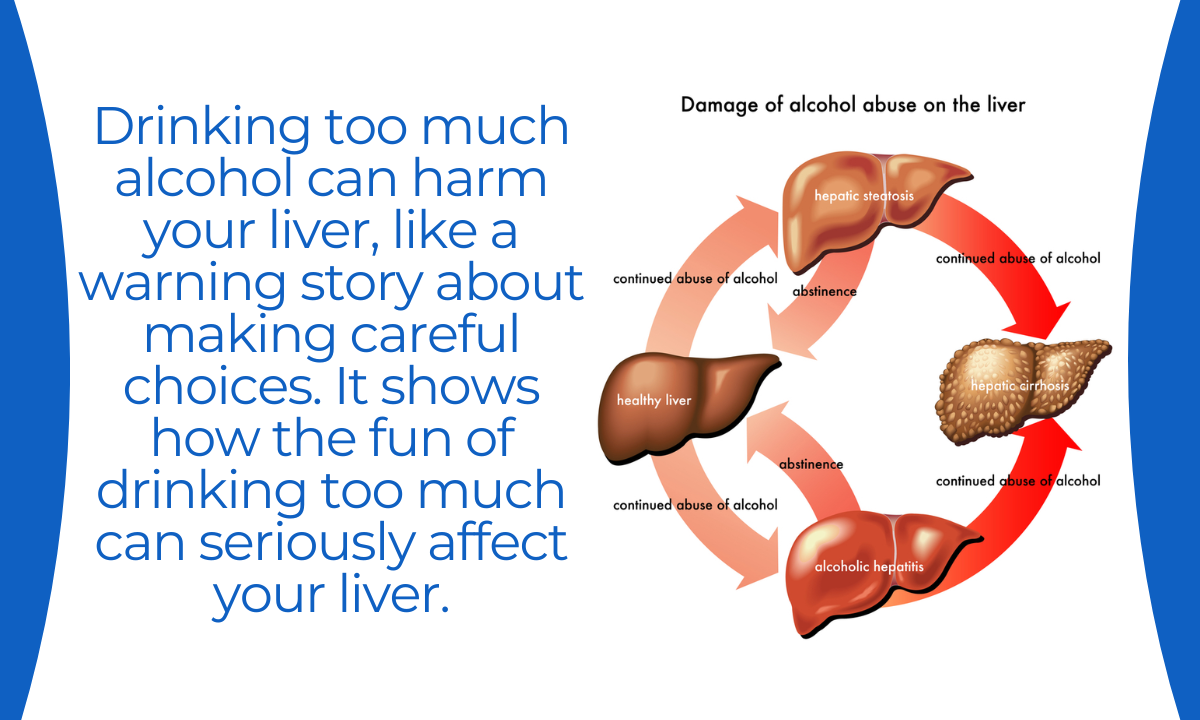
Prevention of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Preventing Alcoholic Hepatitis primarily involves addressing the underlying cause – excessive alcohol consumption:
- Abstinence from Alcohol
- The most effective way to prevent Alcoholic Hepatitis is to abstain from alcohol completely or consume it in moderation.
- Support and Treatment for Alcohol Dependence
- Individuals struggling with alcohol dependence should seek professional help and support to achieve and maintain abstinence.
- Education and Awareness
- Public education campaigns and healthcare initiatives can help raise awareness about the risks associated with heavy alcohol consumption.
Herbal Medicines for Alcoholic Hepatitis
Complementary and alternative therapies, including herbal remedies, are sometimes considered as adjunct treatments for Alcoholic Hepatitis. However, the use of herbal medicines in Alcoholic Hepatitis should be approached with caution and under the guidance of healthcare professionals. Some herbs and supplements that have been studied for their potential benefits in liver health include:
- Milk Thistle (Silymarin)
Milk thistle is one of the most widely used herbal remedies for liver conditions. It has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and is believed to protect liver cells.
- Artichoke (Cynara scolymus)
Artichoke extract is thought to support liver function by enhancing bile production and improving digestion.
- Turmeric (Curcumin)
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, is known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It may benefit liver health.
- Dandelion (Taraxacum officinale)
Dandelion root is believed to have diuretic properties and may support liver health.
- Schisandra (Schisandra chinensis)
Schisandra is an adaptogenic herb that may protect the liver from various toxins.
It’s important to emphasize that while these herbal remedies have shown promise in some studies, their effectiveness can vary between individuals. Consult a healthcare provider before using herbal medicines, especially if you have existing medical conditions or are taking other medications.
Lifestyle Modification for Alcoholic Hepatitis
Lifestyle modifications are crucial for preventing the recurrence of Alcoholic Hepatitis and supporting recovery:
- Abstinence from Alcohol
- Achieving and maintaining complete abstinence from alcohol is the most critical lifestyle modification for individuals with Alcoholic Hepatitis.
- Nutrition and Diet
- Consuming a well-balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can support liver health.
- Weight Management
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is essential, as obesity can contribute to liver damage.
- Regular Exercise
- Regular physical activity can improve overall health and support liver function.
- Stress Reduction
- Reducing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can support recovery.
Conclusion
Alcoholic Hepatitis is a serious and potentially life-threatening liver condition that demands immediate medical attention and appropriate treatment. Understanding the causes, clinical presentation, and treatment options is essential for healthcare professionals and patients.
Complementary therapies, including herbal remedies, may offer some benefits in supporting liver health, but their use should be approached with caution and under the guidance of healthcare providers.
In conclusion, living with or recovering from Alcoholic Hepatitis is a challenging journey. It is essential to work closely with healthcare providers, adhere to prescribed treatments, and make necessary lifestyle modifications to optimize liver health and overall well-being. Achieving and maintaining abstinence from alcohol is crucial for preventing further liver damage and promoting recovery. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are key to ensuring a better quality of life for those affected by this condition.