A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Different Types of Asthma Management Practices, Presentations, Treatments and Prevention
Introduction
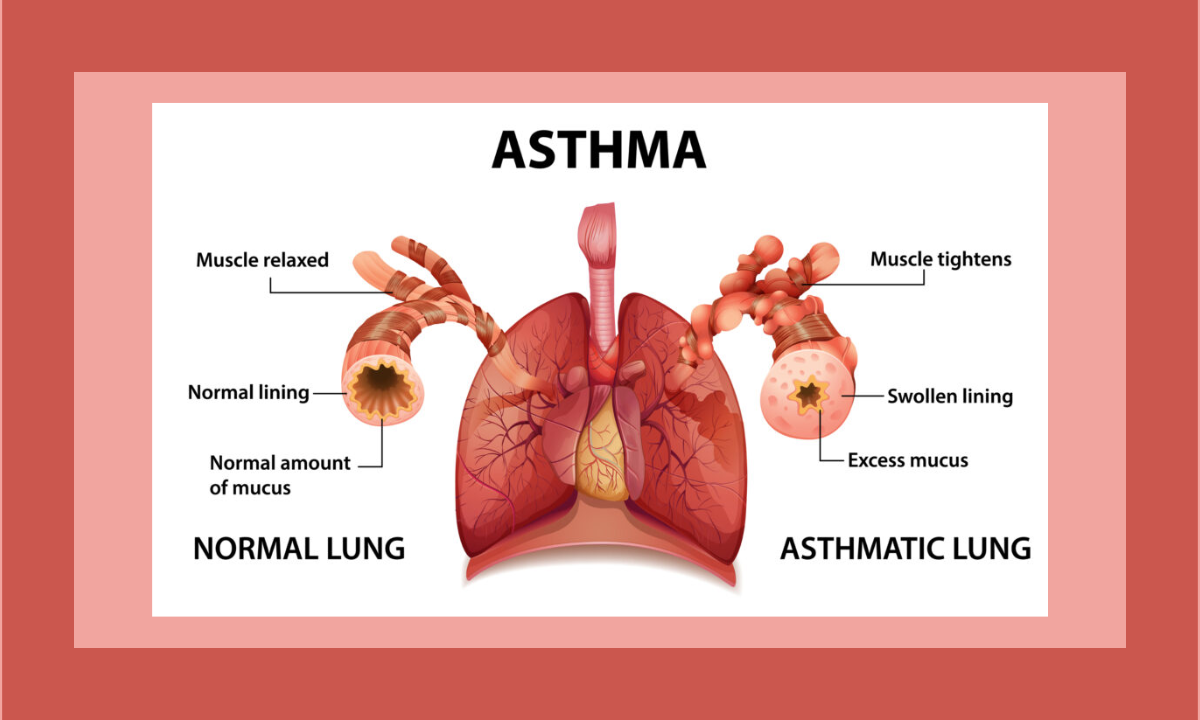
Asthma, a chronic respiratory condition affecting millions worldwide, is a complex and diverse ailment that transcends age, gender, and backgrounds. Its manifestations vary across populations, demanding a nuanced understanding for holistic asthma management. In this in-depth guide, we will embark on an extensive journey into the realm of asthma, placing a spotlight on unique facets like asthma in older adults, asthma during pregnancy, exercise-induced asthma, pediatric asthma, and status asthmaticus. Additionally, we will delve into the significance of public awareness surrounding asthma, the fundamental investigations needed for diagnosis, preventive strategies, conventional treatments, the potential role of herbal remedies, lifestyle modifications, and conclude with a comprehensive perspective on living harmoniously with asthma.

Asthma in Older Adults
Asthma is not confined to youth; it can manifest or persist in older adults, presenting an array of distinct challenges:
- Underdiagnosis: Asthma frequently goes undiagnosed in older adults due to its symptoms, such as shortness of breath and cough, often being erroneously attributed to aging or other health conditions.
- Comorbidities: Older adults with asthma are more susceptible to concomitant illnesses, such as heart disease, which can complicate asthma management.
- Medication Interactions: Asthma medications may interact with drugs prescribed for other age-related conditions, necessitating the utmost vigilance from healthcare providers to minimize adverse effects.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: The management of asthma in older adults often calls for tailored adaptations, including exercises and dietary alterations, to effectively control the condition.
Asthma in Pregnancy
Asthma during pregnancy introduces a multitude of complex considerations:
- Management Challenges: Pregnant individuals with asthma face the intricate task of managing their condition while safeguarding the well-being of their developing fetus.
- Medication Choices: Selecting asthma medications during pregnancy requires extreme care to mitigate potential risks to the unborn child.
- Asthma Triggers: Recognizing and evading asthma triggers, such as allergens or irritants, becomes pivotal during this unique phase of life.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring is of paramount importance to ensure that asthma remains well-controlled throughout the pregnancy.
Exercise-Induced Asthma
Exercise-induced asthma, also known as exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB), is a distinctive condition in which physical activity triggers asthma symptoms:
- Symptoms: The hallmark symptoms of EIB include wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath, which may manifest either during or after exercise.
- Diagnosis: EIB diagnosis relies on exercise challenge tests, where individuals engage in physical activities while their lung function is meticulously monitored.
- Management: Prophylactic measures for EIB include the pre-exercise usage of bronchodilators and customized warm-up routines, pivotal in staving off the occurrence of EIB symptoms.
Pediatric Asthma
Asthma, which can affect individuals of all ages, presents unique considerations when it afflicts children:
- Early Onset: Numerous children develop asthma during their early years, and its severity can fluctuate widely.
- Diagnosis: Accurate diagnosis of asthma in children demands a multifaceted approach, incorporating an in-depth medical history, a thorough physical examination, and lung function tests.
- Treatment: The management of pediatric asthma necessitates the administration of asthma medications tailored to the child’s age and specific triggers. Education of parents and children alike is pivotal for effective asthma management.
Status Asthmaticus
Status asthmaticus stands as a severe and potentially life-threatening form of asthma exacerbation:
- Emergency: Status asthmaticus mandates immediate medical attention and hospitalization, as standard asthma treatments may not suffice to alleviate the life-threatening symptoms.
- Intensive Care: The treatment protocol is intensive and often entails oxygen therapy, intravenous medications, and mechanical ventilation if necessary.
- Prevention: Vigilant adherence to asthma management plans, recognition of early warning signs, and the expedient pursuit of medical care are indispensable in averting status asthmaticus episodes.
Public Awareness about Asthma
Elevated public awareness about asthma is pivotal for various reasons:
- Early Diagnosis: A heightened awareness of the spectrum of asthma symptoms can lead to earlier diagnosis, promoting timely intervention.
- Reduced Stigma: Enhanced awareness can diminish the stigma surrounding asthma, fostering an environment in which individuals are more inclined to seek medical guidance.
- Prevention: An informed public is better equipped to identify asthma triggers and risk factors, potentially averting the onset or exacerbation of asthma.
Basic Investigations for Asthma
Accurate diagnosis and precise assessment of asthma necessitate a battery of comprehensive investigations:
- Pulmonary Function Tests: These evaluations gauge lung capacity, airflow, and the overall functionality of the respiratory system.
- Peak Flow Monitoring: The employment of a peak flow meter empowers individuals to diligently track their lung function and promptly identify worsening asthma symptoms.
- Allergy Testing: The pinpointing of specific allergens via skin or blood tests is instrumental in the management of allergic asthma, facilitating precise avoidance strategies.
- Imaging: Employing technologies such as X-rays and CT scans is paramount for the exclusion of alternative conditions or the evaluation of any lung damage.
Prevention of Asthma
Asthma prevention strategies revolve around the following core principles:
- Allergen Avoidance: The identification and meticulous avoidance of allergens that precipitate asthma attacks is a fundamental tenet of asthma prevention.
- Smoking Cessation: The complete abandonment of smoking and the proactive avoidance of secondhand smoke constitute an integral facet of asthma prevention.
- Vaccinations: The proactive reception of vaccinations is critical to prevent infections that may exacerbate asthma symptoms.
- Asthma Action Plans: The formulation and adherence to personalized asthma action plans, devised in conjunction with healthcare providers, are indispensable for effectual asthma prevention and management.
Conventional Treatment of Asthma
Conventional asthma treatments are multi-pronged and encompass the following approaches:
- Bronchodilators: Both short-acting and long-acting bronchodilators feature prominently in asthma management, functioning to expand the airways and provide relief from acute symptoms.
- Inhaled Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications are the cornerstone of long-term asthma management, curbing airway inflammation effectively.
- Combination Inhalers: For certain cases, combination inhalers, which amalgamate bronchodilators and corticosteroids, are prescribed to optimize asthma control.
- Leukotriene Modifiers: These oral medications, taken on a regular basis, mitigate airway inflammation and are employed in specific asthma cases.
- Biologics: Biologic medications are selectively administered for severe asthma scenarios unresponsive to alternative treatments.
- Oral Corticosteroids: In the throes of severe exacerbations, oral corticosteroids are recommended to suppress inflammation and avert life-threatening asthma episodes.
Herbal Medicines for Asthma
What is the best supplement for asthma? In parallel with conventional treatments, herbal remedies may offer supplementary support:
- Boswellia: Boswellia extract, renowned for its potential anti-inflammatory properties, is thought to alleviate asthma symptoms and reduce airway inflammation.
- Butterbur: Butterbur has garnered attention for its possible role in ameliorating bronchoconstriction, furthering its exploration in asthma management.
- Gingko Biloba: With its noted antioxidant properties, Gingko biloba has been under scrutiny for its potential in abating airway inflammation.
- Licorice Root: The anti-inflammatory attributes of licorice root have piqued interest in its ability to provide relief from asthma symptoms.
Lifestyle Modification for Asthma
Incorporating certain lifestyle changes can significantly contribute to the management and prevention of asthma:
- Allergen Control: The meticulous identification and avoidance of allergens known to trigger asthma, such as dust mites and pet dander, are pivotal.
- Smoking Cessation: The termination of smoking, along with the avoidance of secondhand smoke, is non-negotiable in the realm of asthma management.
- Regular Exercise: The inclusion of moderate, regular exercise in one’s daily routine can foster improved lung function and overall health.
- Stress Management: The adoption of stress-reduction techniques like yoga or meditation is fundamental in preventing asthma exacerbations.
- Dietary Choices: The adherence to a balanced diet replete with fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids not only bolsters overall health but also supports lung function.
Conclusion
Asthma, a multifaceted respiratory condition, unfolds its intricate tapestry through various life stages and scenarios. Be it asthma in older adults, pregnancy, childhood, or the dire status asthmaticus, understanding these unique facets are quintessential for a holistic approach to asthma management. Public awareness, early diagnosis, preventive strategies, and tailored treatment plans are the cornerstones of a harmonious life coexisting with asthma. The multifaceted approach unveiled in this comprehensive guide empowers individuals to assume control over their health, effectively manage their condition, and cherish an improved quality of life despite the challenges posed by asthma.