Silencing the Roar Within: Expert-Backed Techniques for Preventing Tinnitus Forever
Introduction
Tinnitus is a condition characterized by the perception of sound in the absence of any external source. It affects millions of people worldwide and can range from a mild annoyance to a debilitating condition that significantly impacts quality of life. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of tinnitus, explore its various types and symptoms, examine the factors that contribute to its development, discuss prevention strategies, shed light on tinnitus management techniques, highlight the importance of seeking professional help, and explore future directions in tinnitus research.
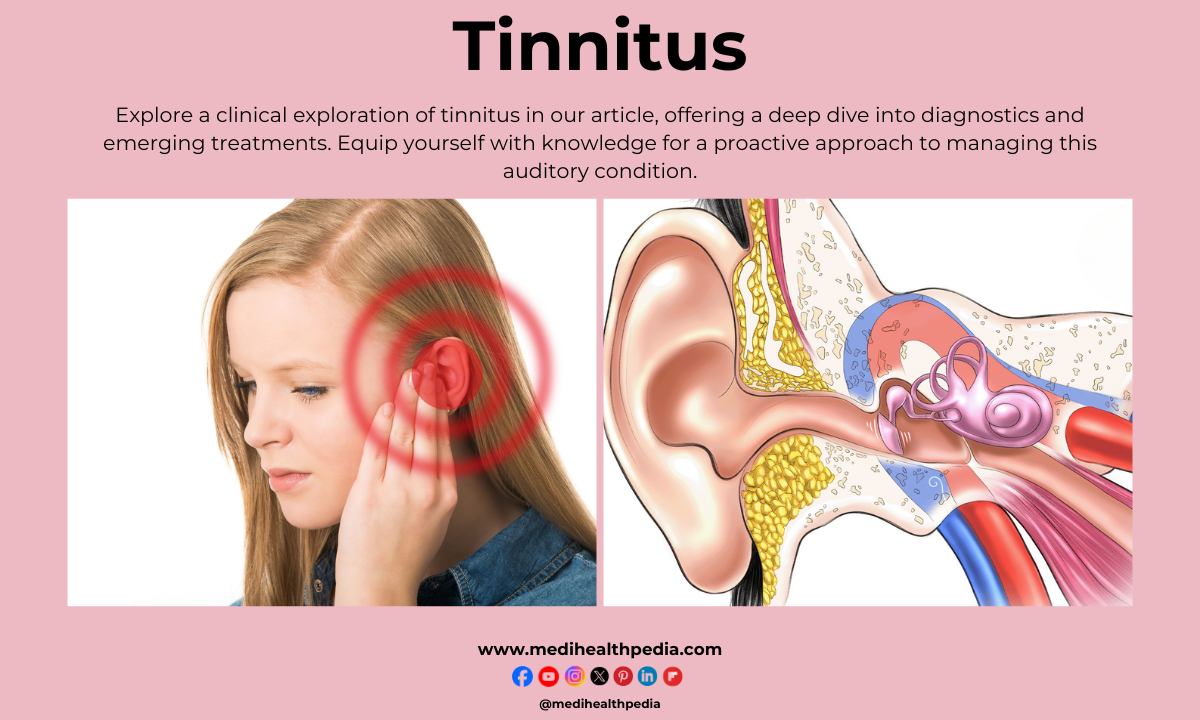
Understanding Tinnitus
Tinnitus is often described as a ringing, buzzing, or humming sound in the ears. However, it is important to note that the perception of sound can vary greatly among individuals. Some may experience a high-pitched whistling, while others may hear a low-frequency pulsing noise. To truly understand tinnitus, it is essential to recognize that it is a symptom rather than a disease in itself. Underlying conditions such as hearing loss, exposure to loud noise, or certain medical conditions can lead to the development of tinnitus.
The Mechanics
Tinnitus occurs when the auditory system, which includes the inner ear and the brain, malfunctions in some way. When sound waves enter the ear, they stimulate the hair cells within the cochlea, a spiral-shaped structure in the inner ear responsible for converting sound into electrical signals. These signals are then transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve, where they are interpreted as sound. In individuals with tinnitus, this normal process is disrupted, resulting in the perception of sound without any external stimulus.
Types and Symptoms of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can manifest in different forms, each with its unique set of symptoms. Subjective tinnitus is the most common type and is only audible to the affected individual. It may be caused by age-related hearing loss, exposure to loud noise, or certain medications. Objective tinnitus, on the other hand, can be heard by both the person experiencing it and others. It is often associated with underlying medical conditions such as vascular disorders or muscle spasms. Common symptoms include ringing, buzzing, hissing, or pulsing sounds in the ears, and in severe cases, it can interfere with concentration, sleep, and overall well-being.
Factors Contributing
Tinnitus can manifest in different forms, each with its unique set of symptoms. Subjective tinnitus is the most common type and is only audible to the affected individual. It may be caused by age-related hearing loss, exposure to loud noise, or certain medications. Objective tinnitus, on the other hand, can be heard by both the person experiencing it and others. It is often associated with underlying medical conditions such as vascular disorders or muscle spasms. Common symptoms include ringing, buzzing, hissing, or pulsing sounds in the ears, and in severe cases, it can interfere with concentration, sleep, and overall well-being.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing tinnitus starts with proactive measures to protect our ears from excessive noise exposure. In the workplace, it is crucial to implement engineering controls, such as installing soundproof materials or maintaining equipment, to minimize noise levels. Providing workers with adequate hearing protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs, can also significantly reduce the risk of tinnitus. Similarly, in recreational settings, individuals should be mindful of noise levels and use earplugs or noise-canceling headphones when required. Regular hearing screenings and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including managing stress and avoiding ototoxic medications, are also essential preventive measures.
Workplace Noise Prevention:
- Implement engineering controls to reduce noise levels.
- Provide workers with proper hearing protection.
- Conduct regular hearing screenings.
Recreational Noise Prevention:
- Be mindful of noise levels in recreational settings.
- Use earplugs or noise-canceling headphones as necessary.
Tinnitus Management Techniques
While prevention is crucial, individuals already experiencing tinnitus can employ various management techniques to alleviate symptoms and improve their quality of life. Sound therapy, which involves the use of background noises to mask the tinnitus sounds, has proven to be effective for many individuals. White noise machines, fans, or specially designed tinnitus maskers can provide relief by diverting attention away from the bothersome sounds. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can also be beneficial in helping individuals develop coping strategies and reduce the impact of tinnitus on their daily lives. Additionally, stress management techniques, relaxation exercises, and support groups can provide emotional support and further aid in tinnitus management.
Natural Remedies for Tinnitus
In the concluding section, we will encapsulate the key points discussed throughout this guide. We’ll reflect on the current state of research and explore the potential future directions in Acne Vulgaris management, including emerging treatments and technologies. We’ll emphasize the importance of personal accountability in managing Acne Vulgaris and maintaining skin health. The management of acne is an ongoing process, and individuals are encouraged to take an active role in their care. With advancements in skincare and
dermatology, the future holds promise for more effective treatments and improved outcomes for individuals with Acne Vulgaris.
Seeking Professional Help
It is important to emphasize that seeking professional help is crucial when dealing with tinnitus. An audiologist or an otolaryngologist can conduct a comprehensive evaluation to determine the underlying cause of tinnitus and develop an individualized treatment plan. They may also address any associated hearing loss and provide recommendations for hearing aids or assistive devices, if necessary. Additionally, they can offer counseling and emotional support, ensuring individuals are well-equipped to manage their tinnitus effectively.
Future Directions
Research into tinnitus continues to advance, with scientists exploring novel approaches to better understand the mechanisms underlying tinnitus and develop more targeted interventions. Recent studies have focused on neurostimulation techniques, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TES), as potential treatment options. Furthermore, advancements in regenerative medicine and gene therapy hold promise for repairing damaged auditory cells and reducing tinnitus symptoms. As research progresses, it is hoped that new treatments will emerge, offering hope for those affected by tinnitus.
Conclusion
Tinnitus is a complex condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. However, by understanding its causes, implementing preventive strategies, and utilizing appropriate management techniques, individuals can effectively cope with tinnitus and mitigate its impact. Seeking professional help plays a crucial role in managing tinnitus, as healthcare professionals can provide tailored treatment plans and offer the necessary support. With ongoing research and advancements, there is hope for improved treatments and ultimately, a future where tinnitus is no longer a source of distress for those affected.
